Diabetic foot ulcers pose a significant risk for individuals living with diabetes, often leading to severe complications if not addressed promptly. Understanding the early signs can make all the difference in preventing further deterioration. Early stage pictures of diabetic foot ulcers serve as vital visual cues, empowering patients and caregivers to recognize these critical warning signs.
Visual references are essential in the journey of managing diabetes-related foot health. By familiarizing themselves with the appearance of early-stage ulcers, individuals can take proactive steps towards treatment and healing. This article aims to provide a closer look at these images, highlighting the importance of early detection and intervention in safeguarding foot health.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers are serious wounds that can develop in individuals with diabetes. Early identification and intervention are crucial for preventing significant complications.
What Are Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that typically form on the foot. Classification distinguishes them into two types: neuropathic ulcers, resulting from nerve damage, and ischemic ulcers, caused by reduced blood flow. They often appear on pressure points, such as the toes or heels, and may be accompanied by signs of infection, including redness or swelling.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of diabetic foot ulcers:
- Neuropathy: Damaged nerves reduce sensation, causing injuries to go unnoticed.
- Poor Circulation: Decreased blood flow impairs healing and increases infection risk.
- High Blood Sugar: Elevated glucose levels delay healing processes.
- Foot Deformities: Bunions or hammer toes can create abnormal pressure points.
- Skin Care Neglect: Infrequent inspection and poor hygiene can lead to infections.
Understanding these causes and risk factors enables effective prevention and management strategies for individuals living with diabetes.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of diabetic foot ulcers is crucial for preventing serious complications. Identifying symptoms promptly can lead to effective treatment and minimize the risk of infection or amputation.
Recognizing Early Symptoms
Recognizing early symptoms of diabetic foot ulcers allows for prompt intervention. Common early signs include:
- Discoloration: Red, brown, or black areas on the foot indicate potential ulceration.
- Swelling: Inflated areas around the toes or heel may signal inflammation.
- Changes in Texture: Rough or scaly skin can suggest developing ulcers.
- Pain or Discomfort: Any unusual pain in the foot may be a warning sign.
- Reduced Sensation: Numbness or tingling suggests nerve damage, leading to undetected injuries.
Regular foot examinations for these symptoms enhance early identification and intervention.
Benefits of Early Treatment
Early treatment of diabetic foot ulcers leads to better outcomes. Key benefits include:
- Reduced Risk of Infection: Prompt attention prevents bacteria growth and infection spread.
- Minimized Tissue Damage: Early intervention can preserve healthy tissue, preventing larger wounds.
- Shorter Healing Times: Targeted treatments in the early stages accelerate recovery.
- Lower Medical Costs: Early management reduces the need for extensive interventions and hospital visits.
- Preserved Mobility: Timely care supports overall foot health and maintains mobility.
Recognizing and managing diabetic foot ulcers at an early stage is essential for effective and efficient care.
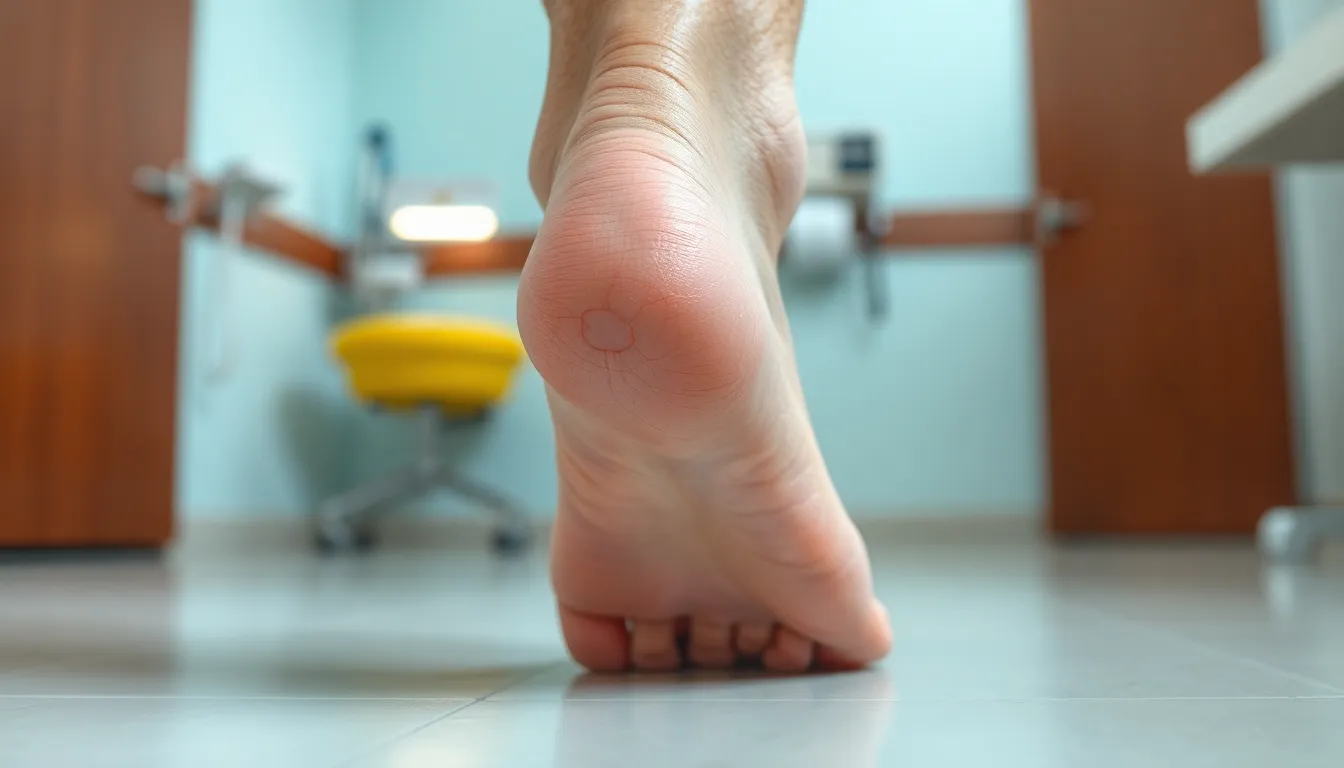
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Early Stage Pictures
Diabetic foot ulcer early-stage pictures serve as vital tools for recognizing and responding to impending complications. These images help highlight visual cues essential for patients and caregivers in identifying ulcers at an early stage.
Visual Identification
Visual identification of diabetic foot ulcers focuses on recognizing specific signs through images. These pictures often depict early-stage ulcers characterized by:
- Discoloration: Affected areas may appear red, brown, or even black, indicating tissue damage.
- Swelling: Increased swelling around the affected site signals inflammation.
- Skin Changes: Changes in texture, such as dryness or cracking, often precede ulcer formation.
- Blisters or Calluses: Presence of blisters or thickened skin can indicate areas at risk for ulceration.
Recognizing these signs visually allows for quicker intervention and treatment.
Common Characteristics
Diabetic foot ulcers exhibit common characteristics that can aid in their early detection. Key features include:
- Wound Size: Small, open sores or abrasions often present at the ulcer’s initial stages.
- Depth: Early ulcers tend to be shallow, affecting only the outer layers of skin.
- Odor: Foul smells may occur as ulcers progress, indicating possible infection.
- Pain or Discomfort: Patients might experience unusual sensations around the ulcer site, though some may report less pain due to neuropathy.
Identifying these characteristics promptly supports effective management and treatment strategies, minimizing the risk of serious complications.
Treatment Options
Early intervention for diabetic foot ulcers significantly improves healing outcomes. Implementing effective treatment strategies ensures that complications remain minimal.
Wound Care Management
Wound care management serves as a fundamental component in treating diabetic foot ulcers. Proper cleaning is essential; using mild soap and water helps prevent infections. Moist wound healing is crucial, thus applying sterile dressings reduces moisture loss and promotes healing.
Regular dressing changes, typically every 1 to 3 days, keep the wound clean and assess progress. It’s important to monitor for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge. Individuals should also manage blood glucose levels diligently, as elevated sugar impairs healing processes. Incorporating offloading techniques, such as specialized footwear or orthotic devices, alleviates pressure on the ulcer, facilitating quicker recovery.
Role of Professional Medical Help
Seeking professional medical help becomes vital when a diabetic foot ulcer is identified. Healthcare providers can offer tailored treatment plans based on the ulcer’s stage and severity. Regular consultations ensure appropriate interventions, such as debridement, which involves removing dead tissue to promote healing.
In cases of severe ulcers, advanced treatments may include antibiotics for infection control or referral to specialists for surgical options. Podiatrists play a key role in monitoring foot health, providing education on proper foot care, and emphasizing the importance of regular foot examinations. Prompt professional intervention not only speeds up recovery but also reduces the risk of serious complications, such as amputation.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing diabetic foot ulcers requires consistent attention to foot care and lifestyle adjustments. Implementing effective strategies significantly reduces the risk of developing these ulcers.
Daily Foot Care Tips
- Inspect feet daily: Regularly check for cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling. Early detection of any abnormalities allows for prompt intervention.
- Keep feet clean and dry: Wash feet with mild soap and warm water daily, ensuring thorough drying, especially between toes. Moisture can lead to fungal infections and ulcer development.
- Moisturize skin: Apply lotion to prevent cracks, avoiding the areas between toes. Cracked skin can create entry points for bacteria.
- Wear proper footwear: Choose well-fitting shoes with adequate support. Avoid walking barefoot to protect feet from injuries.
- Trim toenails carefully: Cut nails straight across and maintain proper length to prevent ingrown nails, which can lead to ulcers.
- Monitor feet temperature: Check for unusual temperature differences between feet. Increased warmth may indicate infection or reduced blood flow.
Lifestyle Changes for Diabetes Management
- Maintain blood glucose levels: Keeping blood sugar within target ranges minimizes the risk of nerve damage and poor circulation, major contributors to foot problems.
- Implement a balanced diet: Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. Proper nutrition supports overall health and glycemic control.
- Engage in regular exercise: Participating in physical activity enhances circulation and supports weight management. Low-impact exercises, such as walking or swimming, are beneficial.
- Avoid smoking: Quitting reduces the risk of vascular complications, improving blood flow and healing capabilities.
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol: Monitor and manage these factors to lower the risk of vascular issues contributing to foot ulcer development.
- Regular healthcare visits: Schedule routine appointments with healthcare providers to monitor diabetes management and receive professional foot evaluations.
Recognizing early signs of diabetic foot ulcers is vital for effective management and prevention of severe complications. Early-stage pictures serve as crucial tools for individuals and caregivers to identify warning signs promptly. By understanding the characteristics of these ulcers and implementing proactive foot care strategies, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of infection and other serious issues.
Maintaining regular foot examinations and seeking professional medical advice ensures tailored treatment plans that cater to each individual’s needs. With proper care and attention, individuals can preserve their mobility and enhance their overall quality of life. Prioritizing foot health is essential for anyone living with diabetes.


